

(Interview from 2016 as part of The Crude Life’s outreach and educational engagement with industrial trades and tech skilled workers of all ages and incomes.)
Michael Smith, Lynnes Welding Training, Bismarck and Fargo, ND, shares his insight on the welding industry and how there is a need for more welders. With the increase in pipes, agriculture and manufacturing in the area, more certified welders are needed.
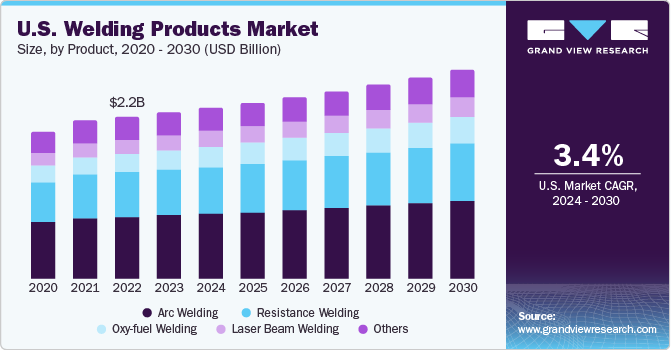
The demand for skilled trade workers, particularly welders, has seen a significant rise over the past two decades. This surge is driven by aging infrastructure, industrial expansion, and a retiring workforce.
To address the shortage, both government programs and private industry have launched numerous initiatives aimed at training new welders and encouraging young people to pursue careers in the trades. Additionally, welding training has undergone substantial evolution, integrating modern technology, improved techniques, and expanded tuition assistance programs.
Industry Expansion and Workforce Shortages
The need for skilled welders spans across industries including construction, manufacturing, aerospace, automotive, and energy sectors. Large infrastructure projects, such as bridge repairs, pipeline construction, and commercial building projects, require a steady supply of certified welders. However, a major challenge facing these industries is the aging workforce, with many experienced welders retiring and not enough new workers entering the trade to replace them.
A report by the American Welding Society (AWS) estimates that by 2028, the U.S. will face a shortage of over 375,000 welders. This growing skills gap has spurred government agencies, trade schools, and businesses to work together in developing training programs and incentives to attract new talent.
Government Programs Promoting Skilled Trades
To combat the labor shortage, federal and state governments have launched several initiatives to promote careers in skilled trades. These programs include:
- Workforce Innovation and Opportunity Act (WIOA) – This federal law provides funding for vocational training programs, including welding certifications, helping unemployed or underemployed individuals gain access to new career opportunities.
- Apprenticeship Programs – The U.S. Department of Labor has expanded registered apprenticeship programs, allowing welders to earn while they learn, gaining hands-on experience while working toward certification.
- Trade School Grants and Scholarships – Government-backed grants, such as the Pell Grant, provide financial aid to students attending trade schools. Additionally, state-level programs offer tuition assistance for welding programs.
- Veterans Training Programs – The GI Bill and similar initiatives help military veterans transition into civilian careers by funding vocational training in high-demand fields like welding.
- State-Sponsored Workforce Development Initiatives – Many states have invested in trade education by partnering with community colleges and vocational schools to expand welding programs and offer incentives to students pursuing careers in the trades.

Advancements in Welding Techniques
Over the past two decades, welding techniques have significantly evolved, making the field more precise and efficient. Some of the notable advancements include:
- Automated and Robotic Welding – Automation has enhanced productivity in manufacturing and large-scale construction, requiring welders to be skilled in programming and operating robotic welding systems.
- Laser and Friction Welding – These high-tech welding methods improve efficiency and precision, reducing waste and enhancing quality.
- Advanced Arc Welding Techniques – Methods like Pulsed Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW-P) and Flux-Cored Arc Welding (FCAW) have become more widely used, improving penetration, reducing defects, and increasing weld strength.
- Underwater and Space Welding – Specialized techniques have developed for extreme environments, expanding welding applications beyond traditional industrial settings.

Integration of Technology in Welding Education
The introduction of new technologies has revolutionized how welding students are trained. Welding education now incorporates:
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) Training – VR welding simulators allow students to practice welding in a safe, controlled environment before handling actual equipment. This reduces material costs and enhances skill development.
- Online Learning Platforms – Many welding schools offer hybrid programs that combine online coursework with hands-on lab training, increasing accessibility for students who cannot attend full-time in-person classes.
- Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and 3D Printing – Students are now trained in using CAD software to design welding projects and in 3D printing technologies that assist with prototyping metal structures.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) Training – With a greater focus on quality control, welders are trained in NDT techniques to inspect weld integrity without damaging the material.
Changes in Training Courses and Curriculum
Welding training has expanded beyond traditional methods to include a more comprehensive curriculum that prepares students for a wider range of industries. Key changes include:
- Expanded Safety Training – With an increased emphasis on workplace safety, welding programs now incorporate more rigorous training in Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) standards and hazard prevention.
- Multi-Process Training – Modern programs train students in multiple welding techniques, making them more versatile and employable.
- Industry-Specific Certifications – Many schools now offer specialized welding certifications tailored to specific industries such as aerospace, nuclear energy, and underwater welding.
- Soft Skills and Business Training – In addition to technical skills, welding programs now incorporate business management and communication training to help welders succeed in leadership roles or entrepreneurship.

Tuition Availability and Financial Assistance
One of the biggest barriers to entering the welding profession has historically been the cost of education. However, funding options have increased significantly, making welding training more accessible:
- Employer-Sponsored Training – Many companies now offer tuition reimbursement programs and apprenticeships where workers can earn certification while employed.
- Scholarships and Grants – Organizations like AWS, SkillsUSA, and local trade unions provide scholarships for welding students.
- Income-Share Agreements (ISAs) – Some welding schools now offer ISAs, where students pay for their education through a percentage of their future earnings instead of upfront tuition costs.
- Community College and Trade School Affordability – Compared to traditional four-year degrees, trade schools and community colleges provide welding programs at a fraction of the cost, making it a more financially viable career path.

The past 20 years have seen a significant transformation in the welding industry, both in terms of workforce demand and training advancements. With strong government and industry-backed initiatives, the barriers to entering the welding profession have decreased, making it an attractive career option for a new generation of workers.
As technology continues to evolve, the future of welding will likely see further automation, improved training methodologies, and expanded job opportunities. With continued investment in vocational education and apprenticeship programs, the welding trade is well-positioned to thrive in the coming decades.
Everyday your story is being told by someone. Who is telling your story? Who are you telling your story to?
Email your sustainable story ideas, professional press releases or petro-powered podcast submissions to thecontentcreationstudios(AT)gmail(DOT)com.
#thecrudelife promotes a culture of inclusion and respect through interviews, content creation, live events and partnerships that educate, enrich, and empower people to create a positive social environment for all, regardless of age, race, religion, sexual orientation, or physical or intellectual ability.

