
Gas combustion engines, also known as internal combustion engines, are the heart of most vehicles on the roads today. These mechanical marvels convert the chemical energy stored in gasoline into mechanical energy, propelling cars, motorcycles, trucks, and many other types of transportation.
Understanding the inner workings of these engines helps us appreciate the engineering brilliance that drives modern transportation.
In this article, we drive into the science and mechanics of how gas combustion engines work.
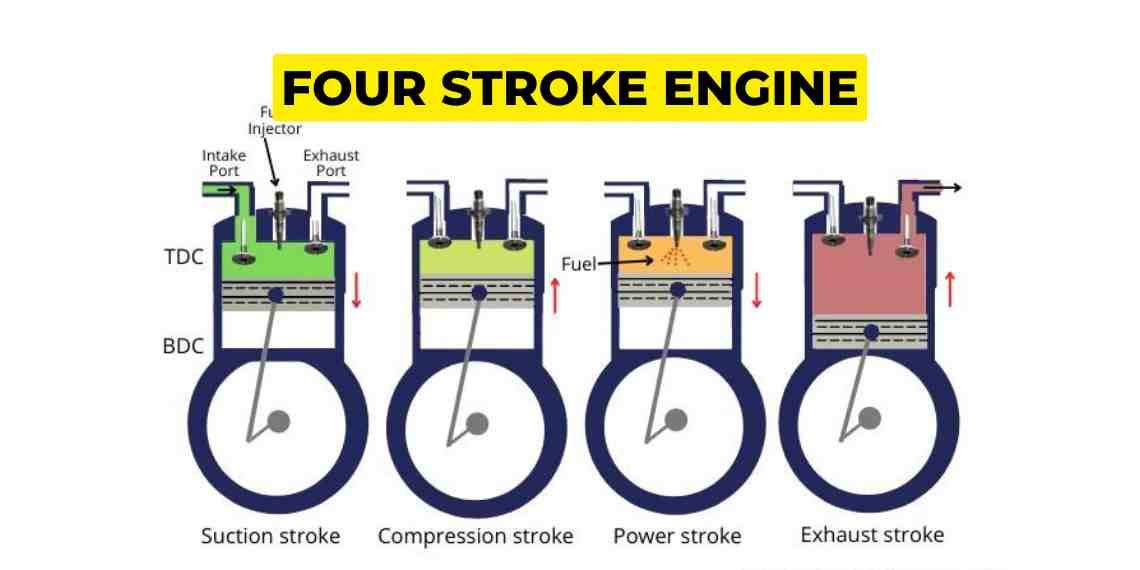
The Four-Stroke Cycle
Most modern gas combustion engines operate on the four-stroke cycle, consisting of four distinct phases: intake, compression, power, and exhaust. Each stroke corresponds to a specific movement of the engine’s piston inside a cylinder. These four strokes together complete one full engine cycle.
Intake Stroke: The cycle begins with the intake stroke. As the piston moves downward inside the cylinder, the intake valve opens, allowing a precise mixture of air and fuel (gasoline vapor) to be drawn into the combustion chamber from the carburetor or fuel injector. This mixture is essential for the subsequent combustion process.
Compression Stroke: Following the intake stroke, the intake valve closes, and the piston moves back up the cylinder, compressing the air-fuel mixture. The purpose of this compression is to increase the mixture’s pressure and temperature, maximizing its potential energy.
Power Stroke: At the top of the compression stroke, when the air-fuel mixture is highly compressed, a spark plug fires an electric spark, igniting the mixture. This ignition causes a rapid and controlled explosion, producing a high-pressure gas that forces the piston downward with tremendous force. This downward movement is known as the power stroke and is the primary source of the engine’s mechanical power.
Exhaust Stroke: Finally, the exhaust valve opens, and the piston moves upward again, pushing out the burned gases from the combustion chamber into the exhaust system. These gases are then expelled through the vehicle’s exhaust pipe.
Camshaft and Timing
The precise timing of the intake and exhaust valve opening and closing is critical for the engine’s efficiency and performance. This timing is controlled by a camshaft, a rotating shaft with eccentric lobes that push against the valves, opening and closing them at specific intervals.
The camshaft is driven by the engine’s crankshaft through a timing belt or chain.
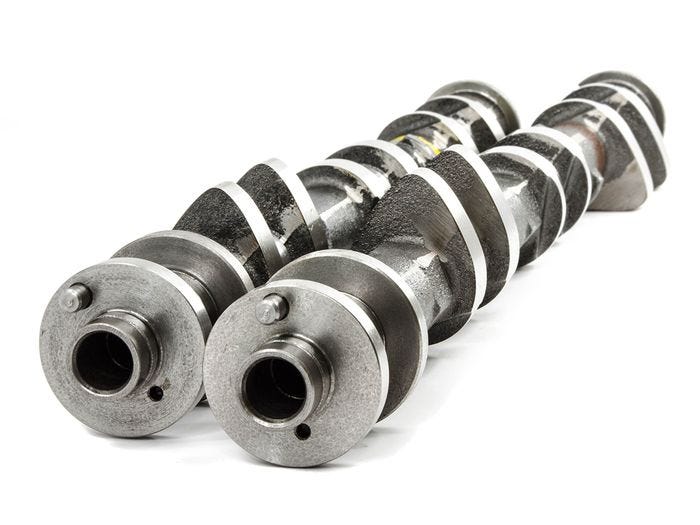

When the engine is operating at different RPMs (revolutions per minute), the camshaft timing must be adjusted accordingly to optimize power and fuel efficiency.
Modern engines often feature variable valve timing systems that can adjust the camshaft’s position in real-time, allowing for better performance across a wide range of engine speeds.
Cooling and Lubrication
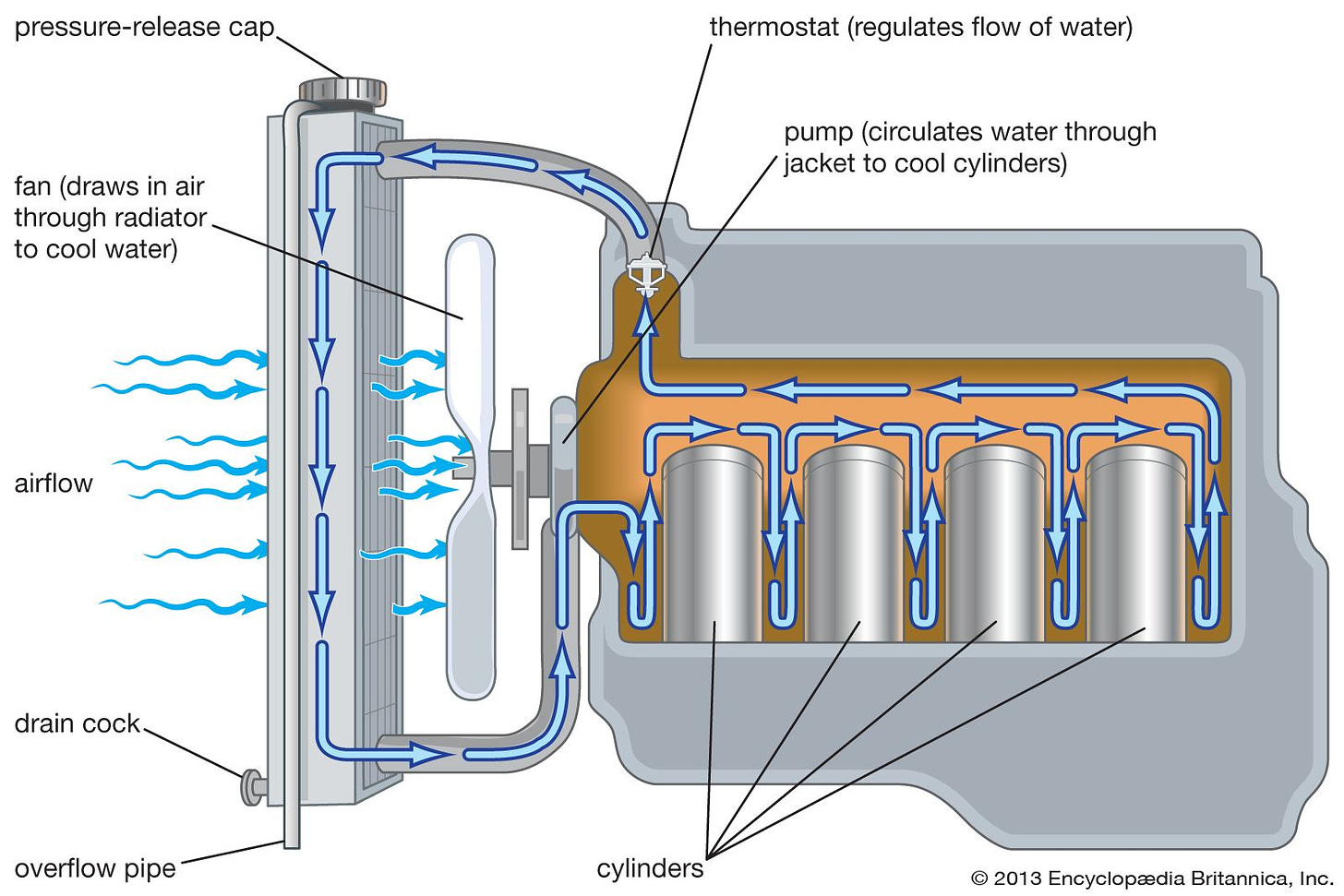
Gas combustion engines generate a significant amount of heat during operation, which can cause damage if not properly managed. To prevent overheating, engines are equipped with cooling systems, typically involving a radiator and coolant fluid. The coolant absorbs heat from the engine and dissipates it through the radiator, helping to maintain an optimal operating temperature.
Lubrication is also crucial to reduce friction between moving parts and prevent wear. Engines use motor oil that circulates throughout the engine, providing a thin film of lubrication between surfaces like the piston and cylinder walls or the crankshaft and bearings.
Conclusion
Gas combustion engines are the backbone of modern transportation, offering an efficient and reliable means of converting gasoline’s chemical energy into mechanical power.
The four-stroke cycle, camshaft timing, cooling, and lubrication systems work in harmony to ensure the engine operates smoothly and efficiently.
As automotive technology continues to advance, engineers are constantly refining and improving gas combustion engines to enhance performance, fuel efficiency, and environmental friendliness.
While electric vehicles are gaining popularity, gas combustion engines will continue to play a significant role in our lives for the foreseeable future. Understanding how they work helps us appreciate the ingenuity behind these remarkable machines that keep us moving forward.
Expert interviews, news updates and multimedia crossovers available upon request.

If you have a news release, energy innovation, story idea, community lifestyle feature, guest, music band or show topic requests, email studio(at)thecrudelife(dot)com
Support the honest hard-working men, women and family who are living The Crude Life today!

About The Crude Life
Award winning interviewer and broadcast journalist Jason Spiess and a team of Content Correspondents engage with the industry’s best thinkers, writers, politicians, business leaders, scientists, entertainers, community leaders, cafe owners and other newsmakers in one-on-one interviews and round table discussions.
The Crude Life has been broadcasting on radio stations since 2011 and posts all updates and interviews on The Crude Life Social Media Network.
Everyday your story is being told by someone. Who is telling your story? Who are you telling your story to?
#thecrudelife promotes a culture of inclusion and respect through interviews, content creation, live events and partnerships that educate, enrich, and empower people to create a positive social environment for all, regardless of age, race, religion, sexual orientation, or physical or intellectual ability.

